A STI Fungus Is Making Itself Cozy in the US
BREAKING: Sexually Transmitted Ringworm Outbreak Sparks Health Alert Across U.S.
In a bizarre and unsettling development that has public health officials on high alert, a rare and aggressive strain of ringworm—scientifically known as Trichophyton mentagrophytes genotype VII, or TMVII—is rapidly spreading through sexual contact, marking one of the most unusual fungal outbreaks in recent U.S. history.
The Minnesota Department of Health has issued an urgent warning after confirming 13 cases and investigating 27 suspected infections of TMVII, primarily concentrated in the Twin Cities metro area since last summer. This marks the largest recorded cluster of the infection in the United States to date, raising alarms among epidemiologists and infectious disease specialists nationwide.
Unlike traditional ringworm, which typically spreads through shared surfaces like gym equipment or contaminated towels, TMVII appears to be transmitted almost exclusively through intimate skin-to-skin contact. The outbreak has predominantly affected men who have sex with men, though health officials stress that anyone engaging in unprotected sexual activity could be at risk.
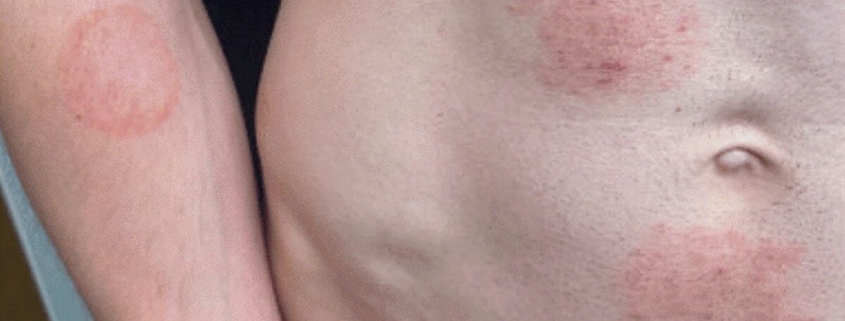
“This is not your ordinary ringworm,” warns Dr. Sarah Thompson, an infectious disease specialist at the University of Minnesota. “TMVII causes intensely painful, inflammatory rashes that can lead to permanent scarring if left untreated. The lesions are often coin-shaped, extremely itchy, and can appear anywhere on the body—but we’re seeing a concerning pattern of genital and buttock involvement.”
The infection manifests as distinctive circular, scaly patches that can be mistaken for other skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis, making accurate diagnosis challenging. What makes TMVII particularly alarming is its resistance to standard antifungal treatments, often requiring prolonged and aggressive medical intervention to fully eradicate.
Health officials are now racing to contain the outbreak through enhanced surveillance and public education campaigns. The Minnesota Department of Health has implemented a mandatory reporting system for suspected cases and is working closely with sexual health clinics to identify and treat infected individuals before the infection spreads further.
“We’re seeing cases that are more severe and persistent than typical ringworm infections,” explains Dr. Michael Chen, the state epidemiologist leading the response. “Patients are experiencing intense burning sensations, significant discomfort, and in some cases, the infection has spread to multiple body sites despite initial treatment attempts.”
The emergence of TMVII represents a troubling evolution in fungal pathogens. First identified in Europe and Asia several years ago, this strain has now established a foothold in North America, suggesting potential adaptation to new environmental conditions and host populations.
Public health experts emphasize that while the overall risk to the general population remains low, certain groups face elevated vulnerability. Individuals using dating apps or engaging in anonymous sexual encounters, those with previous sexually transmitted infections, and men who have sex with men should exercise particular caution.
Prevention strategies recommended by health authorities include avoiding sexual contact when rashes are present, thoroughly covering affected areas with bandages or clothing, refraining from sharing personal items like towels and bedding, and maintaining rigorous hand hygiene after touching potentially infected skin areas.
Treatment typically involves prescription-strength antifungal medications, which must be taken for extended periods to ensure complete elimination of the fungus. Early intervention is crucial to prevent complications and reduce the risk of transmission to sexual partners.
The outbreak has sparked renewed interest in fungal pathogen surveillance and the potential for emerging infectious diseases to spread through unconventional routes. Some researchers speculate that changing sexual behaviors, increased international travel, and evolving fungal resistance patterns may be contributing to the rise of infections like TMVII.
As health departments across the country monitor for potential cases beyond Minnesota, the incident serves as a stark reminder that infectious diseases continue to evolve in unexpected ways. The intersection of sexual health, dermatology, and infectious disease control has never been more critical.
For now, health officials urge anyone experiencing unusual skin rashes, particularly those with recent sexual contact with infected individuals, to seek immediate medical evaluation. The window for effective treatment is narrow, and early diagnosis could prevent both individual suffering and wider community transmission.
The TMVII outbreak represents a new frontier in public health challenges, blending the worlds of sexual health, dermatology, and infectious disease control in ways that demand innovative approaches to prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. As researchers work to understand this emerging threat, one thing is clear: the landscape of fungal infections is changing, and public awareness has never been more crucial.
Tags: #TMVII #RingwormOutbreak #FungalInfection #SexuallyTransmitted #PublicHealthAlert #MinnesotaHealth #EmergingPathogens #SkinInfection #STDWarning #HealthCrisis #InfectiousDisease #MedicalEmergency #SexualHealth #Dermatology #FungalOutbreak #HealthWarning #CDCAlert #MedicalNews #ViralInfection #HealthSafety
Viral Phrases: “Sexually transmitted ringworm spreading across America,” “New fungal threat causes painful, scarring rashes,” “TMVII outbreak largest in U.S. history,” “Ringworm transmitted through sexual contact,” “Minnesota health officials issue urgent warning,” “Emerging fungal pathogen alarms doctors nationwide,” “Coin-shaped rashes signal dangerous new infection,” “Prolonged antifungal treatment required for TMVII,” “Anonymous sexual encounters linked to outbreak spread,” “Permanent scarring possible from aggressive ringworm strain,” “Health departments race to contain unusual fungal outbreak,” “Sexual health clinics on high alert for TMVII cases,” “Changing landscape of infectious disease threats,” “Public education campaign targets high-risk populations,” “Early treatment crucial for preventing complications,” “Fungal resistance patterns evolving rapidly,” “International travel may contribute to pathogen spread,” “Innovative approaches needed for emerging infections,” “Window for effective treatment rapidly closing,” “Medical community mobilizes against unprecedented threat.”
,


Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!