AI-assisted mammograms cut risk of developing aggressive breast cancer
AI-Assisted Mammography Screening Dramatically Reduces Aggressive Cancer Risk, Landmark Study Finds
In a groundbreaking development that could reshape the future of cancer detection, a large-scale randomized controlled trial has demonstrated that artificial intelligence-assisted breast cancer screening significantly reduces the risk of developing aggressive, rapidly-growing tumors between screening rounds. The findings, published in The Lancet Digital Health, represent the first major clinical trial to rigorously evaluate AI’s role in mammography screening.
A New Era in Early Cancer Detection
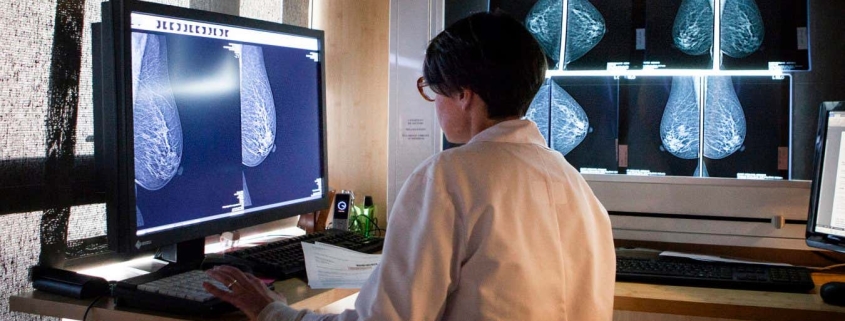
The study, conducted across multiple sites in Sweden with over 100,000 women participating, compared traditional two-radiologist screening methods against an innovative AI-supported approach. The results were striking: women screened with AI assistance were 12% less likely to develop interval cancers—aggressive tumors that emerge between scheduled screening appointments.
“This is the first randomized controlled trial on the use of AI in mammography screening,” explains Kristina Lång, lead researcher at Lund University. “When we got the results, we were extremely thrilled.”
How the AI System Works
The technology, developed by Dutch biotech firm ScreenPoint Medical, employs sophisticated deep learning algorithms trained on more than 200,000 mammography scans from 10 different countries. The system analyzes each mammogram and assigns a cancer likelihood score from 1 to 10 based on subtle visual patterns that might escape human detection.
The workflow is elegantly designed: mammograms scoring 1-9 are reviewed by a single experienced radiologist, while those scoring 10—indicating the highest probability of malignancy—are examined by two radiologists. This triage approach optimizes specialist time while maintaining rigorous safety standards.
Superior Performance, No Trade-offs
An earlier phase of the trial revealed that this AI-assisted method detected 29% more cancers than standard screening protocols, without increasing false-positive rates. “That was terrific,” notes Fiona Gilbert from the University of Cambridge, who was not involved in the research.
The ability to catch more cancers without generating additional false alarms addresses one of the most persistent challenges in mammography screening. False positives can cause unnecessary anxiety, lead to invasive follow-up procedures, and strain healthcare resources.
The Critical Importance of Interval Cancers
Interval cancers represent one of the most concerning failures in screening programs. These aggressive tumors develop rapidly between scheduled screenings, often progressing to advanced stages before detection. Because they grow quickly, they’re more likely to metastasize and carry worse prognoses.
The AI system’s ability to detect these early-stage tumors before they become interval cancers could be life-saving. Lång suggests the AI excels at identifying tiny tumors that human radiologists might miss, particularly those that would later develop into interval cancers.
Real-World Implementation and Global Impact
The trial participants had an average age of 55 and represented diverse populations across Sweden. Half received standard two-radiologist screening, while the other half experienced the AI-assisted approach. The 12% reduction in interval cancers was consistent across the AI-assisted group.
Based on these promising results, Lång anticipates the AI approach will be implemented across southwest Sweden within months. However, she cautions that broader international adoption will require additional country-specific trials.
“Countries need to see what the impact is on their own population, where people are screened more or less often, and are of different ethnicities,” Gilbert emphasizes. The ongoing AI trial in the UK will help address these population-specific questions.
Cost-Effectiveness and Practical Considerations
Economic analysis suggests AI assistance becomes worthwhile if it reduces interval cancer rates by at least 5%. The Swedish trial’s 12% reduction comfortably exceeds this threshold, suggesting strong economic justification for implementation.
Training requirements appear manageable. “The software is fairly easy to use,” Lång notes, suggesting the learning curve for radiologists won’t be prohibitive. However, comprehensive cost-benefit analyses must account for software licensing, hardware requirements, and training programs.
The Human Element Remains Essential
Despite AI’s impressive performance, researchers unanimously agree that human radiologists must remain integral to the screening process. “Women that participate in screening say they do not want to have AI as a standalone tool, they want to have a human in the loop, and I agree with them,” Lång states emphatically.
This sentiment reflects broader concerns about AI autonomy in healthcare. Patients value human judgment, empathy, and the ability to contextualize findings within individual medical histories. The AI system is designed as a powerful tool to augment—not replace—radiological expertise.
Future Research Directions
Several critical questions remain unanswered. The trial didn’t assess whether AI performance varies across different ethnic groups, though researchers acknowledge this as a priority for future studies. Additionally, the impact on less experienced radiologists requires investigation, though Gilbert doesn’t anticipate significant differences.
The technology’s ability to detect extremely early-stage cancers suggests potential applications beyond routine screening, possibly including monitoring high-risk patients or evaluating suspicious findings identified through other means.
A Transformative Moment for Cancer Care
This landmark trial represents more than just incremental improvement in screening technology. It demonstrates AI’s potential to address one of screening’s most persistent failures—interval cancers—while maintaining or improving detection rates for all cancers.
The implications extend beyond breast cancer. If AI can enhance early detection in mammography, similar approaches might benefit other cancer screening programs, potentially transforming cancer care globally.
As healthcare systems worldwide grapple with rising cancer rates and resource constraints, AI-assisted screening offers a compelling solution: better outcomes, improved efficiency, and maintained human oversight. The Swedish trial suggests we may be witnessing the beginning of a new era in cancer detection—one where artificial intelligence and human expertise combine to save more lives than either could achieve alone.
Tags: AI cancer detection, breast cancer screening breakthrough, artificial intelligence healthcare, mammography AI, interval cancer prevention, Swedish medical research, ScreenPoint Medical, early cancer detection technology, AI-assisted radiology, cancer screening innovation, medical AI trials, breast cancer mortality reduction, healthcare AI implementation, Swedish cancer study, AI medical diagnostics, cancer screening cost-effectiveness, human-AI collaboration healthcare, breast cancer early detection, AI screening accuracy, cancer research breakthrough
Viral Sentences: AI detects cancer better than humans, game-changing cancer screening technology, 12% reduction in deadly interval cancers, AI spots tiny tumors radiologists miss, first major AI screening trial proves successful, breast cancer screening revolution begins, AI saves lives in Swedish cancer study, technology that could prevent thousands of cancer deaths, radiologists welcome AI assistance, screening that actually works better, medical breakthrough women have been waiting for, AI that doesn’t replace doctors but makes them better, the future of cancer detection is here, study that will change how we screen for cancer, technology that sees what humans cannot, screening that catches cancer earlier than ever before, AI that reduces false alarms while finding more cancers, breakthrough that could save healthcare systems millions, women prefer AI with human oversight, the 12% difference that could save your life.
,



Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!