Linux Kernel Improvement Can Make Hibernation Several Times Faster With Slow SSDs
Groundbreaking Linux Kernel Patch Promises to Supercharge System Hibernation Speeds
In a remarkable breakthrough for Linux performance optimization, kernel developer Kairui Song has unveiled a game-changing patch series that could revolutionize how quickly Linux systems enter hibernation mode. The development, which has sent ripples through the open-source community, addresses a long-standing bottleneck in Linux’s hibernation performance, particularly benefiting users with slower solid-state drives (SSDs).
The Hibernation Performance Crisis
For years, Linux users with budget or older SSDs have experienced frustratingly slow hibernation times. The issue stems from the kernel’s swap allocator, which historically lacked an optimized allocation path specifically for hibernation operations. This inefficiency became particularly pronounced on drives with poor 4K write performance—a common characteristic of older SATA SSDs and some budget NVMe drives.
The Technical Breakthrough
Song’s solution involves a remarkably elegant approach: optimizing just over two dozen lines of code within the kernel’s swap file management system. The patch introduces a fast allocation path that dramatically accelerates the hibernation process by streamlining how data is written to swap space during the hibernation sequence.
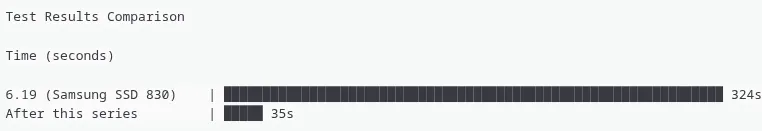
Real-World Performance Gains
The performance improvements are nothing short of extraordinary. In testing with a Samsung 830 SSD—a device that uses the older Serial ATA 2.0 interface—the difference is staggering. Under Linux kernel 6.19, hibernation took a glacial 324 seconds (5 minutes and 24 seconds). With Song’s patches applied, that time plummets to just 35 seconds—a mind-blowing 89% reduction in hibernation time.
While users with modern, high-performance storage devices may see more modest improvements, the impact on systems with slower drives is transformative. As Song notes in his patch submission, “the performance is several times better” for drives with poor 4K write performance.
The Technical Deep Dive
The patch works by creating a specialized allocation strategy for hibernation that bypasses some of the overhead present in the standard swap allocation path. During hibernation, the system must write the entire contents of RAM to disk, and this process becomes bottlenecked when the swap allocator doesn’t have optimizations for this specific use case.
By introducing a hibernation-specific fast path, the kernel can more efficiently queue and write memory pages to disk, reducing the time spent in I/O operations and system calls. The optimization is particularly effective because it targets the exact scenario where performance matters most: when the system is trying to save potentially dozens or hundreds of gigabytes of RAM contents to relatively slow storage.
Timing and Availability
The patches have been submitted for review through the Linux kernel’s established development channels and are currently under evaluation by the kernel community. Unfortunately, they arrived too late to be considered for inclusion in the upcoming Linux 6.20 kernel release. However, there’s optimism that the patches will be ready for the Linux 6.21 release, which typically arrives mid-year.
Broader Implications
This optimization represents more than just a speed improvement—it addresses a fundamental usability issue for Linux users. Fast hibernation is crucial for laptop users who frequently suspend their systems, as well as for desktop users who want quick power-saving transitions. The patch could make Linux hibernation viable on hardware where it was previously too slow to be practical.
Moreover, this development highlights the ongoing commitment of the Linux kernel community to performance optimization, even in areas that might seem niche. The fact that such dramatic improvements can be achieved by modifying just two dozen lines of code is a testament to the kernel’s complexity and the expertise of its developer community.
Looking Ahead
As the patches move through the review process, the Linux community will be watching closely. If accepted, this could mark one of the most significant hibernation performance improvements in recent Linux kernel history. For users with older hardware or budget SSDs, the impact could be transformative, potentially breathing new life into systems that were previously hampered by slow hibernation speeds.
The development also raises interesting questions about other potential optimizations lurking in the kernel’s codebase—areas where targeted improvements could yield outsized performance benefits. As hardware continues to evolve, such optimizations become increasingly important for ensuring that Linux remains competitive with other operating systems in terms of power management and system responsiveness.
Linux hibernation performance
Kairui Song kernel patches
SSD hibernation optimization
Linux swap allocator improvements
faster Linux suspend resume
kernel 6.20 hibernation boost
Samsung 830 SSD optimization
4K write performance Linux
open source performance tuning
Linux power management breakthrough
kernel memory allocation speed
SATA SSD hibernation fix
NVMe hibernation performance
Linux sleep mode acceleration
kernel developer optimization techniques
system resume time reduction
Linux storage performance
hibernation time improvement
kernel code optimization
Linux 6.21 features
slow SSD hibernation fix
memory to disk speed
Linux power saving performance
kernel patch review process
open source hibernation
system sleep acceleration
Linux performance engineering
storage device optimization
kernel hibernation path
swap file optimization
Linux laptop performance
system suspend speedup
kernel development breakthrough
hibernation bottleneck fix
Linux memory management
SSD write performance
kernel code review
Linux power efficiency
system resume optimization
hibernation sequence improvement
Linux kernel performance
storage I/O optimization
power management Linux
system sleep enhancement
kernel hibernation fix
Linux user experience improvement
open source kernel optimization
hibernation time reduction
Linux system responsiveness
,


Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!