NASA used Claude to plot a route for its Perseverance rover on Mars
NASA’s Perseverance Rover Achieves Historic Milestone: First AI-Planned Drive on Mars
In a groundbreaking achievement that marks a new era in space exploration, NASA’s Perseverance rover has successfully completed its first autonomous drive entirely planned by an artificial intelligence system. This historic feat, accomplished in December 2024, represents a significant leap forward in how we navigate and explore distant worlds.
From Human-Guided to AI-Assisted Exploration
Since its dramatic landing on Mars in February 2021, Perseverance has been a marvel of engineering and scientific discovery. The rover has sent back the first-ever audio recordings from the Martian surface, collected rock samples for eventual return to Earth, and captured stunning imagery of the Red Planet’s landscape. Now, it’s making history again by becoming the first NASA rover to have its route planned by an AI chatbot.
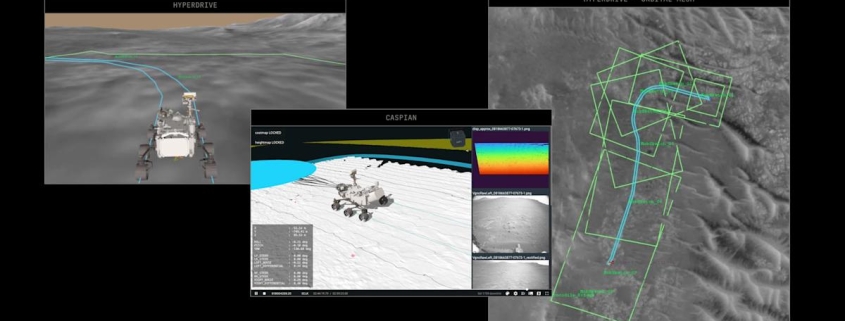
The journey took place between December 8 and 10, 2024, when Perseverance navigated approximately 400 meters (about 437 yards) through a challenging field of rocks in Jezero Crater. What makes this drive remarkable is that the entire route was plotted by Claude, the AI chatbot developed by Anthropic, rather than the traditional human-operated planning process.
The Complexity Behind AI Route Planning
Planning a route for a Mars rover is far from simple. NASA engineers typically spend considerable time and effort creating what they call a “breadcrumb trail” of waypoints for the rover to follow. This process involves analyzing images from space, combined with the rover’s onboard cameras, to ensure safe passage across the Martian terrain.
The AI-assisted approach required a sophisticated collaboration between human expertise and machine learning capabilities. NASA first provided Claude Code, Anthropic’s programming agent, with years of contextual data from the rover’s previous operations. This extensive training period allowed the AI to understand the complexities of Martian terrain navigation.
Once equipped with this knowledge, Claude began the mapping process methodically, creating waypoints in ten-meter segments. The AI didn’t just generate a single route; it critiqued and iterated on its own work, refining the path to ensure optimal safety and efficiency.
Human Oversight and Validation
Despite the AI’s capabilities, NASA maintained its rigorous safety protocols. Engineers from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) carefully reviewed Claude’s proposed route before sending any commands to Perseverance. They ran the AI-generated waypoints through their standard simulation software, which they use daily to verify the accuracy of commands sent to the rover.
The validation process revealed that Claude’s planning was remarkably accurate. NASA engineers reported that they only needed to make “minor changes” to the AI-generated route. One adjustment was necessary because the team had access to ground-level images that Claude hadn’t seen during its planning phase, highlighting the importance of human oversight even with advanced AI systems.
Doubling Efficiency and Scientific Discovery
The implications of this successful AI-assisted drive are profound for future Mars exploration. NASA estimates that using Claude for route planning will cut the planning time in half while making the journeys more consistent. This efficiency gain translates directly into increased scientific productivity.
“Less time spent doing tedious manual planning — and less time spent training — allows the rover’s operators to fit in even more drives, collect even more scientific data, and do even more analysis,” NASA explained. “It means, in short, that we’ll learn much more about Mars.”
This efficiency becomes even more critical given the challenges NASA faces. The agency lost approximately 4,000 employees in 2024 due to budget cuts, representing about 20 percent of its workforce. While Congress ultimately rejected proposals to cut NASA’s science budget by nearly half, the agency is operating with significantly reduced resources compared to previous decades.
Anthropic’s Rapid AI Evolution
For Anthropic, this achievement represents a stunning validation of their AI technology’s capabilities. Just last spring, Claude struggled with relatively simple tasks like playing Pokémon Red on a Game Boy. In less than a year, the same AI system has progressed from failing at an 8-bit video game to successfully plotting navigation routes for a rover on another planet.
This rapid advancement demonstrates the accelerating pace of AI development and its potential applications in fields requiring complex decision-making and spatial reasoning. NASA is already looking ahead, expressing excitement about future collaborations. “Autonomous AI systems could help probes explore ever more distant parts of the solar system,” the agency noted, suggesting that this is just the beginning of AI-assisted space exploration.
The Future of Space Exploration
The successful integration of AI into Mars rover operations opens up new possibilities for space exploration. As missions venture further into the solar system, communication delays with Earth become more significant. An AI system capable of making real-time navigation decisions could be crucial for exploring distant moons, asteroids, and eventually, other planets.
This achievement also highlights the growing importance of human-AI collaboration in scientific endeavors. Rather than replacing human expertise, AI systems like Claude are augmenting human capabilities, allowing scientists and engineers to focus on higher-level analysis and discovery while the AI handles routine but complex tasks like route planning.
The Perseverance rover’s AI-assisted drive represents more than just a technological milestone; it’s a glimpse into the future of space exploration, where artificial intelligence and human ingenuity work together to push the boundaries of what’s possible in our quest to understand the universe.
Tags & Viral Phrases:
Mars rover AI navigation, NASA Perseverance breakthrough, Claude chatbot space exploration, AI planned route Mars, Jezero Crater autonomous driving, Anthropic NASA collaboration, space exploration AI revolution, Mars surface navigation AI, future of planetary exploration, AI in space science, Perseverance historic achievement, autonomous space robotics, NASA efficiency breakthrough, AI transforming space missions, Mars exploration technology leap, Claude Code NASA success, space AI milestone, interplanetary AI navigation, Mars rover productivity boost, AI space exploration future, NASA AI partnership, autonomous planetary navigation, space robotics AI advancement, Mars mission AI integration, Claude AI space success, NASA workforce challenges, AI space exploration efficiency, future Mars missions AI, space science AI collaboration
,



Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!